Datatables is a plug-in to enhance the HTML table interaction and provide adaptable tools. Datatables CRUD (Create, Retrieve Update Delete) will improve your application in terms of readability, Better UI, and other advantages. There are many benefits of using this plug-in, but for this tutorial, we will be discussing a simple Create, Retrieve, Update, and Delete (CRUD).
Table of Content
- Introduction
- Configure Database
- Setting assets file and project folder
- Database Connection
- Create Member
- Retrieve Data
- Remove Member
- Update Member
1. Introduction
In this section, we are going to develop a CRUD (Create, Retrieve, Update, Delete) PHP operation with the Datatable jquery plugin which will improve the table flexibility. In the future as a web developer, you will be working with these basic functionalities namely create, retrieve, update, and delete. The CRUD logic is relevant to CRUD with PHP MYSQLI Tutorial. The Ajax and Datatables are only used to raise the performance of CRUD operations. To understand how CRUD operation works in the Datatable jquery plugin, We recommend you go through each part of this tutorial.
The below video illustrates the final system of this tutorial. The source code of this application will be provided at the end of this tutorial.
2. Configure Database
Database Name: datatables_crud
Table Name: members
Table Column: id, name, contact, address, active
To create the database for this tutorial, you can either download the SQL command by clicking the button which is provided at the end of this tutorial or manually copy and paste the following SQL command into your MYSQL database.
CREATE DATABASE `datatables_crud`;
CREATE TABLE `datatables_crud`.`members` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`fname` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`lname` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`contact` varchar(20) NOT NULL,
`active` int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT '1',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1 AUTO_INCREMENT=3 ;
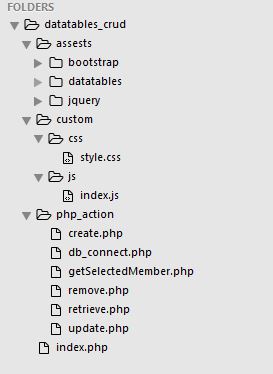
3. Setting assets file and project folder
In this part, we will be creating a folder and file within this project folder. In this project, there will be three folders and one file. First of all, create three folders and a file namely assets, custom, and php_action and index.php as a file i.e. : [datatables_crud/assests], [datatables_crud/custom], [datatables_crud/php_action], and [datatables_crud/index.php].
Firstly, In an assets folder, bootstrap, datatables, and jquery files are included. Please download the files and keep them in this folder. Secondly, In a custom folder, CSS and js folder are required and within that folder, each folder contains one file i.e. [datatables_crud/custom/css/style.css] and [datatables_crud/custom/js/index.js] respectively. Finally, The php_action folder which includes six files and they are create.php, db_connect.php, getSelectedMember.php, remove.php, retrieve.php, and update.php.
If you have followed the steps correctly then the working folders and files structure would look like the below:
4. Database Connection
In db_connect.php file i.e. [php_action/db_connect.php], contains a database connection. In this application, the db_connect.php file will be used to perform any action for CRUD. Such as connecting to the database, executing the query, and closing the connection. If you have a different database name for this tutorial, please change the name of the database in the db_connect.php file which is highlighted below.
<?php
$servername = "127.0.0.1";
$username = "root";
$password = "";
$dbname = "datatables_crud";
// create connection
$connect = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// check connection
if($connect->connect_error) {
die("Connection Failed : " . $connect->connect_error);
} else {
// echo "Successfully Connected";
}
?>
5. Create Member
5.1 Add Member Button and Linking to Assets file
To start with inserting the member’s information into the system, First of all, we’ll create a bootstrap pop-up modal containing the input fields within a form and go to index.php file i.e. [datatables_crud/index.php], and add an “Add Member” button at the top of the table. Please check your index.php file plugin’s link which is necessary to run the various plugin for this tutorial.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CRUD SYSTEM</title>
<!-- bootstrap css -->
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="assests/bootstrap/css/bootstrap.min.css">
<!-- datatables css -->
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="assests/datatables/datatables.min.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-12">
<center><h1 class="page-header">CRUD System <small>DataTables</small> </h1> </center>
<div class="removeMessages"></div>
<button class="btn btn-default pull pull-right" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#addMember" id="addMemberModalBtn">
<span class="glyphicon glyphicon-plus-sign"></span> Add Member
</button>
<br /> <br /> <br />
<table class="table" id="manageMemberTable">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>S.no</th>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Address</th>
<th>Contact</th>
<th>Active</th>
<th>Option</th>
</tr>
</thead>
</table>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- add modal -->
<div class="modal fade" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" id="addMember">
<div class="modal-dialog" role="document">
<div class="modal-content">
<div class="modal-header">
<button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="modal" aria-label="Close"><span aria-hidden="true">×</span></button>
<h4 class="modal-title"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-plus-sign"></span> Add Member</h4>
</div>
<form class="form-horizontal" action="php_action/create.php" method="POST" id="createMemberForm">
<div class="modal-body">
<div class="messages"></div>
<div class="form-group"> <!--/here teh addclass has-error will appear -->
<label for="name" class="col-sm-2 control-label">Name</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="name" name="name" placeholder="Name">
<!-- here the text will apper -->
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="address" class="col-sm-2 control-label">Address</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="address" name="address" placeholder="Address">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="contact" class="col-sm-2 control-label">Contact</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="contact" name="contact" placeholder="Contact">
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="active" class="col-sm-2 control-label">Active</label>
<div class="col-sm-10">
<select class="form-control" name="active" id="active">
<option value="">~~SELECT~~</option>
<option value="1">Activate</option>
<option value="2">Deactivate</option>
</select>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="modal-footer">
<button type="button" class="btn btn-default" data-dismiss="modal">Close</button>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Save changes</button>
</div>
</form>
</div><!-- /.modal-content -->
</div><!-- /.modal-dialog -->
</div><!-- /.modal -->
<!-- /add modal -->
<!-- jquery plugin -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="assests/jquery/jquery.min.js"></script>
<!-- bootstrap js -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="assests/bootstrap/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
<!-- datatables js -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="assests/datatables/datatables.min.js"></script>
<!-- include custom index.js -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="custom/js/index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
Copy and paste these codes into your index.php file and navigate to this page. Click on add member button to inspect if the bootstrap modal is working correctly.
5.2 Creating a PHP file to insert the data into the database
In these codes, the insert process happens. Look through the codes and we will go through them afterward:
<?php
require_once 'db_connect.php';
//if form is submitted
if($_POST) {
$validator = array('success' => false, 'messages' => array());
$name = $_POST['name'];
$address = $_POST['address'];
$contact = $_POST['contact'];
$active = $_POST['active'];
$sql = "INSERT INTO members (name, contact, address, active) VALUES ('$name', '$contact', '$address', '$active')";
$query = $connect->query($sql);
if($query === TRUE) {
$validator['success'] = true;
$validator['messages'] = "Successfully Added";
} else {
$validator['success'] = false;
$validator['messages'] = "Error while adding the member information";
}
// close the database connection
$connect->close();
echo json_encode($validator);
}
Let us look at the beginning of the codes, It checks if the form is submitted by using a $_POST global variable. If the form is submitted then it inserts the data into the database and checks if the query is executed successfully. At the end of the query, the built-in json_encode function will pass the result of the action.
5.3 Create an Ajax file to pass the data to the server
<?php
// global the manage memeber table
var manageMemberTable;
$(document).ready(function() {
manageMemberTable = $("#manageMemberTable").DataTable();
$("#addMemberModalBtn").on('click', function() {
// reset the form
$("#createMemberForm")[0].reset();
// remove the error
$(".form-group").removeClass('has-error').removeClass('has-success');
$(".text-danger").remove();
// empty the message div
$(".messages").html("");
// submit form
$("#createMemberForm").unbind('submit').bind('submit', function() {
$(".text-danger").remove();
var form = $(this);
// validation
var name = $("#name").val();
var address = $("#address").val();
var contact = $("#contact").val();
var active = $("#active").val();
if(name == "") {
$("#name").closest('.form-group').addClass('has-error');
$("#name").after('The Name field is required');
} else {
$("#name").closest('.form-group').removeClass('has-error');
$("#name").closest('.form-group').addClass('has-success');
}
if(address == "") {
$("#address").closest('.form-group').addClass('has-error');
$("#address").after('The Address field is required');
} else {
$("#address").closest('.form-group').removeClass('has-error');
$("#address").closest('.form-group').addClass('has-success');
}
if(contact == "") {
$("#contact").closest('.form-group').addClass('has-error');
$("#contact").after('The Contact field is required');
} else {
$("#contact").closest('.form-group').removeClass('has-error');
$("#contact").closest('.form-group').addClass('has-success');
}
if(active == "") {
$("#active").closest('.form-group').addClass('has-error');
$("#active").after('The Active field is required');
} else {
$("#active").closest('.form-group').removeClass('has-error');
$("#active").closest('.form-group').addClass('has-success');
}
if(name && address && contact && active) {
//submi the form to server
$.ajax({
url : form.attr('action'),
type : form.attr('method'),
data : form.serialize(),
dataType : 'json',
success:function(response) {
// remove the error
$(".form-group").removeClass('has-error').removeClass('has-success');
if(response.success == true) {
$(".messages").html('<div class="alert alert-success alert-dismissible" role="alert">'+
'<button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="alert" aria-label="Close"><span aria-hidden="true">×</span></button>'+
'<strong> <span class="glyphicon glyphicon-ok-sign"></span> </strong>'+response.messages+
'</div>');
// reset the form
$("#createMemberForm")[0].reset();
// reload the datatables
manageMemberTable.ajax.reload(null, false);
// this function is built in function of datatables;
} else {
$(".messages").html('<div class="alert alert-warning alert-dismissible" role="alert">'+
'<button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="alert" aria-label="Close"><span aria-hidden="true">×</span></button>'+
'<strong> <span class="glyphicon glyphicon-exclamation-sign"></span> </strong>'+response.messages+
'</div>');
} // /else
} // success
}); // ajax subit
} /// if
return false;
}); // /submit form for create member
}); // /add modal
});
The manageMemberTable is initiated as a global variable to call in another function. This concept will be cleared up in the next part. The #addMemberModalBtn click function will clear the input field and inside that function, the #createMemberForm onsubmit function will validate the input field and send the data into the server with the help of Ajax when the form is submitted by users.
6. Retrieve Data
This part is easy, go to the [custom/js/index.js] file, and in that file, we will need to call the [php_action/retrieve.php] file. In this section, there are two steps to fetch the data from the database. Look through the codes and we will go through them afterward:
<?php
require_once 'db_connect.php';
$output = array('data' => array());
$sql = "SELECT * FROM members";
$query = $connect->query($sql);
$x = 1;
while ($row = $query->fetch_assoc()) {
$active = '';
if($row['active'] == 1) {
$active = '<label class="label label-success">Active</label>';
} else {
$active = '<label class="label label-danger">Deactive</label>';
}
$actionButton = '
<div class="btn-group">
<button type="button" class="btn btn-default dropdown-toggle" data-toggle="dropdown" aria-haspopup="true" aria-expanded="false">
Action <span class="caret"></span>
</button>
<ul class="dropdown-menu">
<li><a type="button" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#editMemberModal" onclick="editMember('.$row['id'].')"> <span class="glyphicon glyphicon-edit"></span> Edit</a></li>
<li><a type="button" data-toggle="modal" data-target="#removeMemberModal" onclick="removeMember('.$row['id'].')"> <span class="glyphicon glyphicon-trash"></span> Remove</a></li>
</ul>
</div>';
$output['data'][] = array(
$x,
$row['name'],
$row['address'],
$row['contact'],
$active,
$actionButton
);
$x++;
}
// database connection close
$connect->close();
echo json_encode($output);
?>
Firstly, In the above codes, the data is fetched from the database and stored as an associative array. The fetched data is appended into an array variable. At the end of the script, the fetched data is converted into a JSON format. The bootstrap dropdown button which includes the javascript onclick function will be justified in the next part.
Secondly, This is the most important part. We will be using an “Ajax” built-in function of a datatable to retrieve the data from the server i.e. retrieve.php file. To use the Ajax function, we will be writing a bit of code where the datatable function is instantiated. Look through the highlighted code.
manageMemberTable = $("#manageMemberTable").DataTable({
"ajax": "php_action/retrieve.php",
"order": []
});
A video demonstration to retrieve a data through datatable function.
7. Remove Member
Go to the index.php file in [datatables_crud/index.php]. The logic is simple. First of all, we’ll create a remove button to pop up a modal with a confirmation button. Secondly, we’ll create a server-side processing script file that will remove the selected member’s information from the database Lastly, submit the form via Ajax.
7.1 Creating the remove modal form
Go to the index.php file and create a pop-up bootstrap modal with a confirmation button inside a form. When the remove button is clicked this remove confirmation modal should be displayed. For now, Copy and paste them into the index.php file after adding the modal code.
<!-- remove modal -->
<div class="modal fade" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" id="removeMemberModal">
<div class="modal-dialog" role="document">
<div class="modal-content">
<div class="modal-header">
<button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="modal" aria-label="Close"><span aria-hidden="true">×</span></button>
<h4 class="modal-title"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-trash"></span> Remove Member</h4>
</div>
<div class="modal-body">
<p>Do you really want to remove ?</p>
</div>
<div class="modal-footer">
<button type="button" class="btn btn-default" data-dismiss="modal">Close</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" id="removeBtn">Save changes</button>
</div>
</div><!-- /.modal-content -->
</div><!-- /.modal-dialog -->
</div><!-- /.modal -->
<!-- /remove modal -->
7.2 Creating the remove.php file
Go to remove.php in the php_action folder. Copy and paste these codes into the remove.php file.
<?php
require_once 'db_connect.php';
$output = array('success' => false, 'messages' => array());
$memberId = $_POST['member_id'];
$sql = "DELETE FROM members WHERE id = {$memberId}";
$query = $connect->query($sql);
if($query === TRUE) {
$output['success'] = true;
$output['messages'] = 'Successfully removed';
} else {
$output['success'] = false;
$output['messages'] = 'Error while removing the member information';
}
// close database connection
$connect->close();
echo json_encode($output);
?>
7.3 Creating the remove function in Ajax
In this part, create a javascript function as remove member.
[css autolinks=”false” classname=”myclass” collapse=”false” firstline=”1″ gutter=”true” highlight=”” htmlscript=”false” light=”false” padlinenumbers=”false” smarttabs=”true” tabsize=”4″ toolbar=”true” title=”custom/js/index.js”]
// global the manage memeber table
var manageMemberTable;
$(document).ready(function() { …
});
function removeMember(id = null) {
if(id) {
// click on remove button
$("#removeBtn").unbind(‘click’).bind(‘click’, function() {
$.ajax({
url: ‘php_action/remove.php’,
type: ‘post’,
data: {member_id : id},
dataType: ‘json’,
success:function(response) {
if(response.success == true) {
$(".removeMessages").html(‘<div class="alert alert-success alert-dismissible" role="alert">’+
‘<button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="alert" aria-label="Close"><span aria-hidden="true">×</span></button>’+
‘<strong> <span class="glyphicon glyphicon-ok-sign"></span> </strong>’+response.messages+
‘</div>’);
// refresh the table
manageMemberTable.ajax.reload(null, false);
// close the modal
$("#removeMemberModal").modal(‘hide’);
} else {
$(".removeMessages").html(‘<div class="alert alert-warning alert-dismissible" role="alert">’+
‘<button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="alert" aria-label="Close"><span aria-hidden="true">×</span></button>’+
‘<strong> <span class="glyphicon glyphicon-exclamation-sign"></span> </strong>’+response.messages+
‘</div>’);
}
}
});
}); // click remove btn
} else {
alert(‘Error: Refresh the page again’);
}
}
8. Update Member
8.1 Creating update modal form and fetching particular member data
In this part, we are going to get the particular member’s information whenever the edit button is clicked. When clicking that button the editMember function is invoked and it will fetch the member’s information for displaying in the input fields and updating the member’s information.
The logic is simple, In index.js create an editMember method which should accept one parameter namely member id. By using that id it should be able to fetch and display the member’s information with the help of Ajax. As well as we need to create a pop-up modal on the index page i.e. index.php to display and update the member’s information. To do this, we need to write some codes in getSelectedMember.php, index.js, and index.php files.
Firstly, go to the getSelectedMember.php file which is located at [php_action/getSelectedMember.php]. This code will retrieve a particular member’s information from the database by using the particular member’s id. Copy and paste these codes and we will go through them afterward:
<?php
require_once 'db_connect.php';
$memberId = $_POST['member_id'];
$sql = "SELECT * FROM members WHERE id = $memberId";
$query = $connect->query($sql);
$result = $query->fetch_assoc();
$connect->close();
echo json_encode($result);
?>
In the above codes, the server gets the member id from the $_POST variable. Through that id, the script executes the query and returns the associative data into a JSON format.
Secondly, Go to the index.js file which is located at [custom/js/index.js]. In this file, an editMember method will get a member id and pass it to the server for getting the data. Copy and paste these codes and we will go through them afterward:
// global the manage memeber table
var manageMemberTable;
$(document).ready(function() {...
});
function removeMember(id = null) { ...
}
function editMember(id = null) {
if(id) {
// remove the error
$(".form-group").removeClass('has-error').removeClass('has-success');
$(".text-danger").remove();
// empty the message div
$(".edit-messages").html("");
// remove the id
$("#member_id").remove();
// fetch the member data
$.ajax({
url: 'php_action/getSelectedMember.php',
type: 'post',
data: {member_id : id},
dataType: 'json',
success:function(response) {
$("#editName").val(response.name);
$("#editAddress").val(response.address);
$("#editContact").val(response.contact);
$("#editActive").val(response.active);
// member id
$(".editMemberModal").append('<input type="hidden" name="member_id" id="member_id" value="'+response.id+'"/>');
} // /success
}); // /fetch selected member info
} else {
alert("Error : Refresh the page again");
}
}
In the above codes, the editMember function requires one parameter as member id. From that id, the function will fetch the member information, display the value in the input field and create a hidden input field with the member id value.
8.2 Submitting the form via Ajax
In this section, when a form is submitted, the onsubmit function is invoked. This function will verify the input field and update the member’s information.
Firstly, go to the [custom/js/index.js] file and copy and paste the highlight codes inside the editMember function as below and we’ll go through them afterward:
function editMember(id = null) {
if(id) {
// remove the error
$(".form-group").removeClass('has-error').removeClass('has-success');
$(".text-danger").remove();
// empty the message div
$(".edit-messages").html("");
// remove the id
$("#member_id").remove();
// fetch the member data
$.ajax({
url: 'php_action/getSelectedMember.php',
type: 'post',
data: {member_id : id},
dataType: 'json',
success:function(response) {
$("#editName").val(response.name);
$("#editAddress").val(response.address);
$("#editContact").val(response.contact);
$("#editActive").val(response.active);
// mmeber id
$(".editMemberModal").append('<input type="hidden" name="member_id" id="member_id" value="'+response.id+'"/>');
// here update the member data
$("#updateMemberForm").unbind('submit').bind('submit', function() {
// remove error messages
$(".text-danger").remove();
var form = $(this);
// validation
var editName = $("#editName").val();
var editAddress = $("#editAddress").val();
var editContact = $("#editContact").val();
var editActive = $("#editActive").val();
if(editName == "") {
$("#editName").closest('.form-group').addClass('has-error');
$("#editName").after('<p class="text-danger">The Name field is required</p>');
} else {
$("#editName").closest('.form-group').removeClass('has-error');
$("#editName").closest('.form-group').addClass('has-success');
}
if(editAddress == "") {
$("#editAddress").closest('.form-group').addClass('has-error');
$("#editAddress").after('<p class="text-danger">The Address field is required</p>');
} else {
$("#editAddress").closest('.form-group').removeClass('has-error');
$("#editAddress").closest('.form-group').addClass('has-success');
}
if(editContact == "") {
$("#editContact").closest('.form-group').addClass('has-error');
$("#editContact").after('<p class="text-danger">The Contact field is required</p>');
} else {
$("#editContact").closest('.form-group').removeClass('has-error');
$("#editContact").closest('.form-group').addClass('has-success');
}
if(editActive == "") {
$("#editActive").closest('.form-group').addClass('has-error');
$("#editActive").after('<p class="text-danger">The Active field is required</p>');
} else {
$("#editActive").closest('.form-group').removeClass('has-error');
$("#editActive").closest('.form-group').addClass('has-success');
}
if(editName && editAddress && editContact && editActive) {
$.ajax({
url: form.attr('action'),
type: form.attr('method'),
data: form.serialize(),
dataType: 'json',
success:function(response) {
if(response.success == true) {
$(".edit-messages").html('<div class="alert alert-success alert-dismissible" role="alert">'+
'<button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="alert" aria-label="Close"><span aria-hidden="true">×</span></button>'+
'<strong> <span class="glyphicon glyphicon-ok-sign"></span> </strong>'+response.messages+
'</div>');
// reload the datatables
manageMemberTable.ajax.reload(null, false);
// this function is built in function of datatables;
// remove the error
$(".form-group").removeClass('has-success').removeClass('has-error');
$(".text-danger").remove();
} else {
$(".edit-messages").html('<div class="alert alert-warning alert-dismissible" role="alert">'+
'<button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="alert" aria-label="Close"><span aria-hidden="true">×</span></button>'+
'<strong> <span class="glyphicon glyphicon-exclamation-sign"></span> </strong>'+response.messages+
'</div>')
}
} // /success
}); // /ajax
} // /if
return false;
});
} // /success
}); // /fetch selected member info
} else {
alert("Error : Refresh the page again");
}
}
First of all, the edit member function gets the member id as a parameter, and through that id, it retrieves the member’s information. When the users submit the form, the submit function is invoked to verify the input field and update the member information.
This part is simple, we’re going to add the codes to the update.php file to update the member information in the database. Just copy and paste them into your update.php file and we’ll go through them afterward:
<?php
require_once 'db_connect.php';
//if form is submitted
if($_POST) {
$validator = array('success' => false, 'messages' => array());
$id = $_POST['member_id'];
$name = $_POST['editName'];
$address = $_POST['editAddress'];
$contact = $_POST['editContact'];
$active = $_POST['editActive'];
$sql = "UPDATE members SET name = '$name', contact = '$contact', address = '$address', active = '$active' WHERE id = $id";
$query = $connect->query($sql);
if($query === TRUE) {
$validator['success'] = true;
$validator['messages'] = "Successfully Added";
} else {
$validator['success'] = false;
$validator['messages'] = "Error while adding the member information";
}
// close the database connection
$connect->close();
echo json_encode($validator);
}
?>
Download Source Code !!!
Download